Mein Versuchsaufbau besteht aus:
- 1 x Arduino Uno-Nachbau von AZ-Delivery
- 1 x Joystick aus Freenove Starterpaket
- Kabel
Verwendete Software:
- Arduino IDE 1.8.16
- Quellcode aus dem Freenove Tutorial
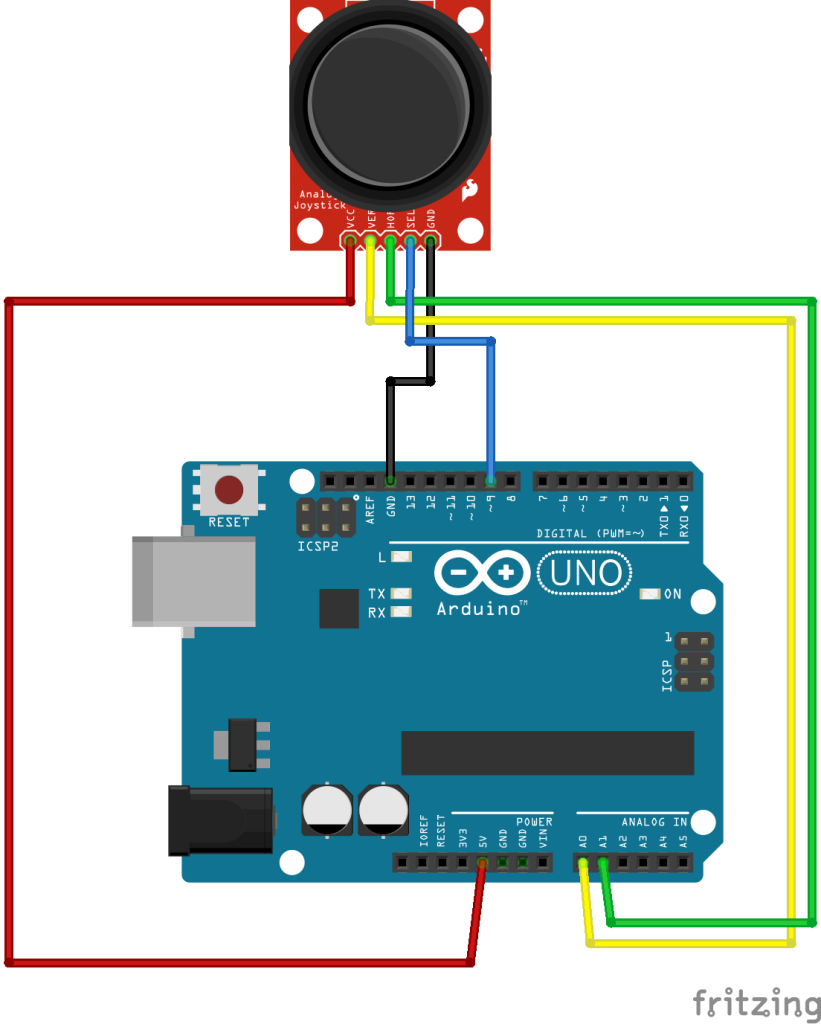
Anschlussplan:
Folgender Quellcode wurde verwendet:
int xAxisPin = 0; // define X pin of Joystick
int yAxisPin = 1; // define Y pin of Joystick
int zAxisPin = 8; // define Z pin of Joystick
int xVal, yVal, zVal; // define 3 variables to store the values of 3 direction
void setup()
{
pinMode(zAxisPin, INPUT_PULLUP); // initialize the port to pull-up input
Serial.begin(115200); // initialize the serial port with baud rate 115200
Serial.println("UNO is ready!"); // print the string "UNO is ready!"
}
void loop()
{ // read analog value in XY axis
xVal = analogRead(xAxisPin);
yVal = analogRead(yAxisPin); // read digital value of switch in Z axis
zVal = digitalRead(zAxisPin); //print the data read above
Serial.print("X : ");
Serial.print(xVal);
Serial.print(" \t Y : ");
Serial.print(yVal);
Serial.print(" \t Z : ");
Serial.println(zVal);
delay(200);
}
Fazit:
Der Joystick erfüllt im Prinzip seinen Zweck, allerdings stimmen die Anschläge nicht mit den Min-/Maxwerten von 0 bzw. 1024 überein.